The Veterinary Laboratories VIP plus proceeded to the acquisition of an automated method for conducting plenty of microbiological analysis in companion animals and in livestock. The advantages especially concerning the susceptibility testing in relation to the previous method of disk diffusion are mainly:
- The test is done with a much greater number of antibiotics (previously 6-8 compared to up to 20 at present)
- The Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) is given allowing the clinician to choose the most effective of the antimicrobial
agents to whom the isolated are susceptible.
In this way the Veterinary Laboratories contribute in the selection of the most effective antibiotic by the clinical veterinarian that is able to include MIC, the outbreaks of the infection and the clinical Break Points.
Additionally a successful therapeutic outcome reduces the chances of appearance of microbiological resistance.
WHAT IS MIC
It’s called the minimum concentration (in µg/ml) of an antibiotic that can inhibit the growth of a specific microorganism
In the above example MIC of the bacterium is 64 ug/ml of the tested antimicrobial agent.
CLINICAL CATEGORIES / CLSI DEFINITONS
• Susceptible (S)
High possibility of response to the treatment
• Resistant (R)
The therapy is likely to fail
• Intermediate (I)
It would be better not to be selected in case other antibiotics show susceptibility in the test report.
However they can be effective when:
- Administration of higher doses
- They concentrate in higher density in a body fluid
THE REPORT OF THE LABORATORY RESULTS
The report that follows includes the entire list of antibiotics that have been tested and it is likely tovary depending the bacterium is Gram (such as below), Gram + or Streptococcus. MIC of isolated microorganism is recorded separately for each antimicrobial agent that exists along with the R (resistant), I (intermediate) or S (sensitive). In some cases the quantitive results are not reported for some antibiotics. They usually are observed where there is no relevance between the microorganism and the antimicrobial agent. Also when the
clinical interpretation R is not accompanied by MIC is due to the endogenous endurance of the bacterium to the specific antibiotic.
WHAT IS THE RELATION BETWEEN MIC AND CLINICAL RESISTANCE
Only MIC is able to define the effectiveness of an antibiotic in a clinical case.
The Clinical Breakpoint (BP) identifies if a culture is susceptible, intermediate, and resistant. It is based in:
- The distribution of MIC in a bacterial population. MIC90 is the concentration cival που αναστέλλει την ανάπτυξη του 90% of a specific strain of microorganism (Pharmacodynamic criteria)
- The maximum concentration of an antibiotic in plasma or tissues, Cmax. (Pharmacodynamic criteria)
The Clinical Breakpoints are defined by national committees such as CSLI (Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute) or EUCAST (European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing) that issue instructions.
HOW MIC IS USED FOR THE SELECTION OF THE MOST APPROPRIATE ANTIMICROBIAL FACTOR
MIC that is recorded in the results report is possible to be compared with the Clinical Break point for every antimicrobial factor.
In this way if MIC of the isolated microorganism is bigger or equal with the Clinical Breakpoint of the specific factor, then the bacterium shows clinical resistance. In case that MIC is smaller than the Clinical Breakpoint then the bacterium shows clinical sensitivity.
In most cases the microorganism develops sensitivity in many antibiotics. The following example describes the way that MIC can be used for the selection of the most appropriate antimicrobial factor:
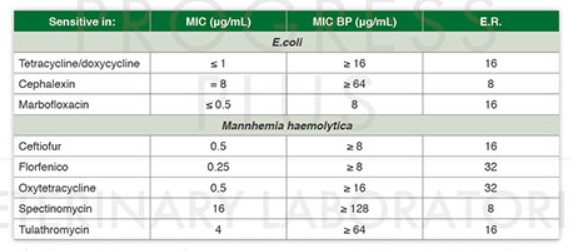
If E.coli is sensitive in three antibiotics based on MIC, Tetracycline / Doxycycline and Marbofloxacin are considered effective.
But taking into account the Clinical Breakpoints we observe that Tetracycline is possible to be more appropriate because there is a difference 16X between MIC and Clinical Breakpoint in relation with a difference of 8X of Marbofloxacin.
The Laboratories VET IN PROGRESS PLUS in the new form of the results report, except for MIC will include in a separate sheet the efficiency ratio E.R.
So the Veterinarian in combination with other pharmacokinetic/ pharmacodynamic parameters will have an extra useful “tool in the selection of the most appropriate antibiotic
ANTIBIOTICS
The detection of the outbreak of the infection plays significant role in the selection of the antibiotic, the selection of the dose and the route of administration.The reason is that in order to have a successful therapy, the antibiotic must achieve satisfactory concentration in the outbreak of infection, that must exceed MIC of the responsible for the infection microorganism, For example lipophilic antibiotics pass more easily through the membranes and achieve bigger concentration in the tissues than in blood serum. Medications that are renally excreted reach higher levels in bladders than the ones in blood. Also some antibiotics are more effective in Gram. bacteria than in Gram- and vice versa
Finally some antimicrobial agents are used as markers in order to define the sensitivity of other similar ones. For example, oxacillin controls the presence of MRSA
Cephalexin: Sensitivity in all cephalosporins except for celazon.
Clindamycin: Sensitivity in lincomycin. It must not be used in horses, rabbits, and other herbivores. It is not effective in Gram- aerobic bacteria.
Erythromycin: Sensitivity in azithromycin and clanthromycin It is not effective in Gram aerobic bacteria
Gentamicin synergy: It is controlled only in cases of Enterococcus app. If there is resistance amoxicillin and sensitivity in gentamicin aynergy, in cases of serious infections it is possible to administrate amoxicillin, ampicillin or penicillin in combination with gentamicin
Tetracycline: Sensitivity in doxycycline and minocycline It is not recommended in young animals.
Trìmethoprim/Sulfa: Sensitivity in other sulfonamides
- Laboratories:
- Vet in Progress Plus
- Service:
- Bacteriology - Mycology
- Category:
- Interpretation Of Susceptibility Testing



