With this procedure proteins are separated in blood serum, urine and other collections e.g. peritoneal fluid, main protein fractions
ELECTROPHORESIS INDICATIONS
- Findings of pathological values of proteins in serum
- Presence of Infections
- Investigation of possible multiple myeloma or recurrent infection
IMMUNOBLOTTING INDICATIONS
- When a pathological “zone” of monoclonal immunoglobulin has been found in electrophoresis
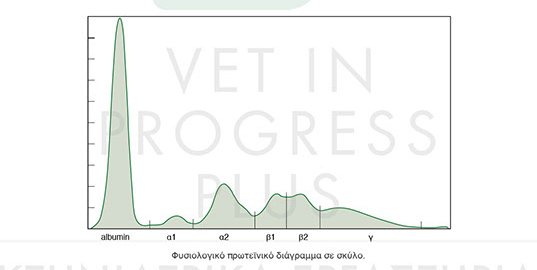
MAIN PROTEINS IN BLOOD SERUM THAT ARE VISIBLE WITH ELECTROPHORESIS
- ALBUMIN
A decreased level may be caused by malnutrition, decreased composition in liver and increased
loss from gastrointestinal track or urinary system. Increased level of albumin is common in cases of dehydration.
- ALPHA-GLOBULINS
They are composed in liver and include proteins of acute phase, alpha-2 macroglobulin and haptoglobin. In most species they are separated in two main fractions alpha-1 and alpha-2, though further divisions are observed in some animal species and occasionally in humans. An increase in alpha-1 and especially in alpha-2 globulins is considered important and is related to acute inflammatory diseases.
- BETA-GLOBULINS
They are usually composed in liver and they include fibrinogen (plasma), transferrin and C3, C4 complement components. They are separated in beta-1 and beta-2, like alpha globulins, in most animal species. In dogs a further division in beta-1a and beta 1b is observed Increased levels of beta-globulins may be non-specific, but there were reported in liver diseases, pyoderma and nephritic syndromes. Sometimes pointed elevations in this zone may be caused by a protein by multiplying a clone of plasma cells, as it happens in multiple myeloma or lymphosarcoma
- GAMMA-GLOBULINS
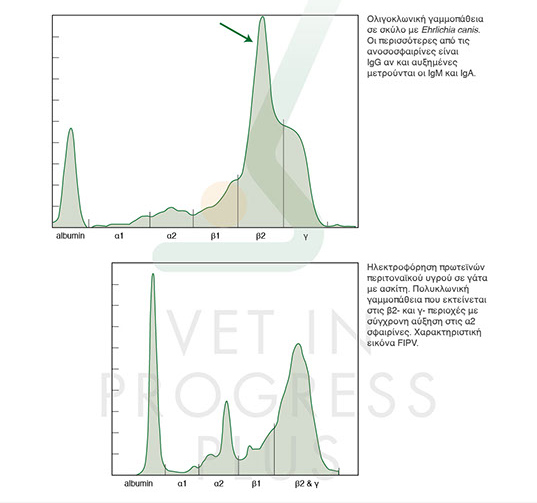
Gamma globulins include the immunoglobulins IgG, IgA and IgM, though the last two often immigrate in the zone of beta-2 or in the beginning of gamma globulins. Not only the increase but also the shape of the elevation provides diagnostic information. Wide elevation shows polyclonal gammopathy which is usually associated with antigen irritation and is not indicative. High and sharp elevation shows monoclonal gammopathy because of cancerous lesions such as multiple myeloma of beta cells or chronic lymphocytic leukemia. There are some cases of sharp elevations that are called oligocional gammopathy and refer to various diseases such as Ehrlichia, Leishmania. FIV, FIP e.t.c
CONDITIONS OF SAMPLE:
- Serum (not plasma, that includes fibrinogen/beta-2 and gamma zone)
- Serum that is not hemolytic or lipemic zone
- Small amount of samples
- Laboratories:
- Vet in Progress Plus
- Service:
- Serology & Immunology
- Category:
- Protein Electrophoresis