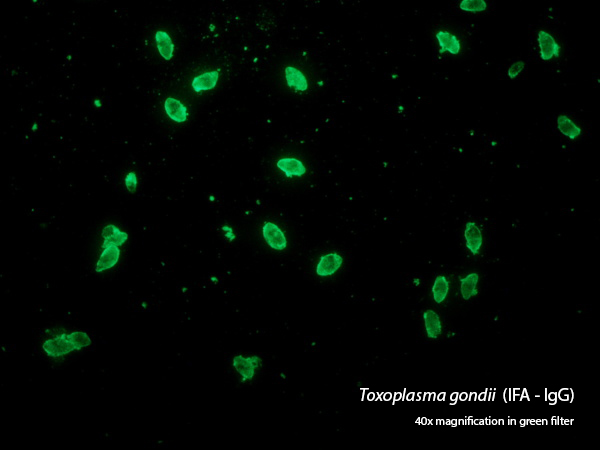
DIAGNOSIS OF TOXOPLASMOSIS IN CATS USING THE METHOD OF IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE OR / AND REAL TIME POLYMERASE CHAIN REACTION
Dimitra Bitchava, Theodora Irene Adam, Katerina Spilioti, Konstantina Bitchava
• Animal and Human Disease with global spread
• Zoonosis
• Cause: Toxoplasma gondii, intracellular protozoan
• Final and intermediate host: cats and other felines
• Intermediate hosts: Various animal species and Humans
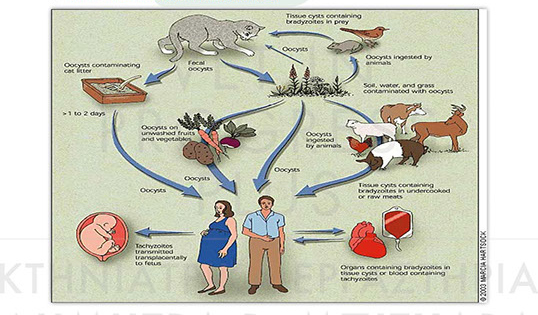
BIOLOGICAL CYCLE OF THE PARASITE
RECOMMENDED DIAGNOSTICS FROM O.I.E (WORLD ORGANIZATION FOR ANIMAL HEALTH)
- Isolation of the parasite
- Direct detection of the parasite in tissues, coatings and biological materials
- Molecular techniques
- Antibody detection
I. Neutralizing (Sabin – Feldman Dye Test)
II. Indirect Immunofluorescence (IFA)
III. Agglutinin reactions (DA, AC/HS)
IV. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
LABORATORY INVESTIGATION OF 70 DOMESTIC CATS
- Period of 1 year
- Animals aged from 1 to 9 years from all breeds
- Aim
I. Differential diagnosis of clinical disease in cats
II. Precautionary
FOLLOWED METHODOLOGY
- Specification of antibodies
I. Specification of IgG antibodies
II. Specification of IgM antibodies - Real-time PCR in focal samples
LABORATORY TEST RESULTS
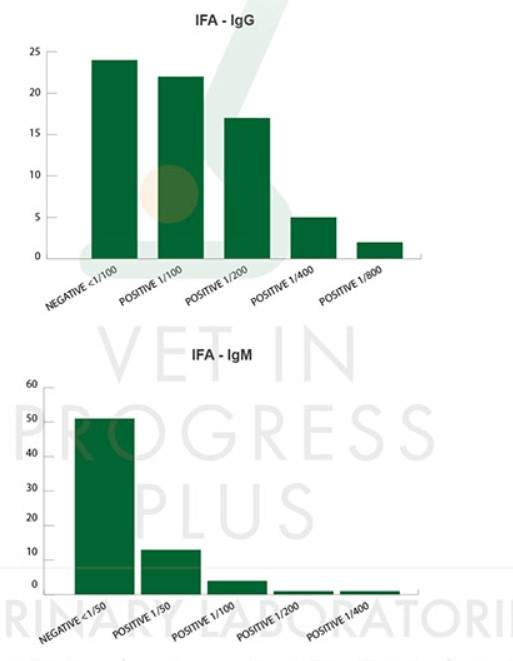
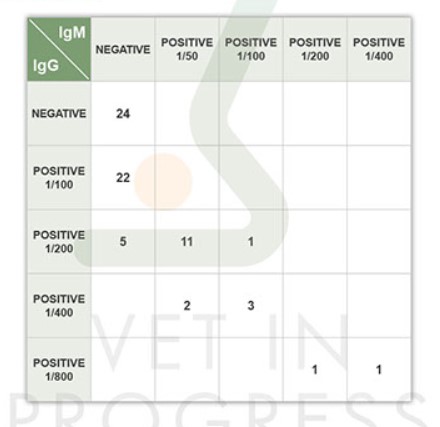
CORRELATION OF IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE RESULTS FOR IGG/IGM ANTIBODIES
RESULTS OF REAL-TIME PCR IN FECAL SAMPLES OF ALL TESTED CATS
• Negative→ 62 negative in IFA – IgG/M
• Posstive→ 4 titled IFA – IgG 1/200
• Posstive→ 3 titled IFA – IgG 1/400
• Posstive→ 1 titled IFA – IgM 1/100
- Laboratories:
- Vet in Progress Plus
- Service:
- Serology & Immunology
- Category:
- Toxoplasmosis